Describe How a Light Microscope Creates a Magnified Image
Focus the light from a bright source onto the. A light microscope focuses a light source at a specimen through a series of lenses.

Light Microscopes An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
The classic compound microscope magnifies in two steps.
. What is a light microscope. Its an upright microscope that produces a two-dimensional image and has a higher magnification than a stereoscopic microscope. Body tube Body tube can be monocular binocular and the combine photo-binocular also called trinocular.
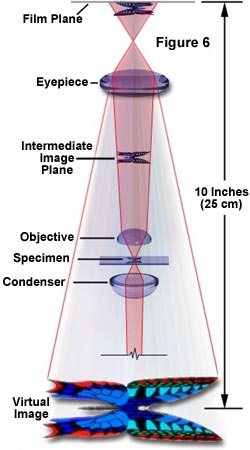
It does this by creating a magnified image through the use of a series of glass lenses which first focus a beam of light onto or through an object and convex objective lenses to. You can calculate the total magnifying power of the microscope by multiplying the magnifying powers of the objective lens and the eyepiece so 10 x 40 total magnification of 400x. Most light microscopes are compound microscope that contains at least two lenses.
The microscope is able to create a 3-D picture of the specimen based on the way the electrons bounce off it. Light from a mirror is reflected up through the specimen or object to be viewed into the powerful objective lens which produces the first magnification. The microscope is an optical instrument that uses a lens or a combination of lenses to produce magnified image of small object.
Pick up the light transmitted by the specimen C. Binocular tubes have provision for inter-pupillary distance. First with an objective lens that produces an enlarged image of the object in a real image plane.
This produces a detailed colored three-dimensional image and has high resolution. The picture appears on a monitor. Describe how a light microscope creates a magnified image.
A scanning electron microscope provides a much better resolution than a compound light microscope. Monocular binocular and Trinocular. In the optical microscope visible light rays reflected from or transmitted by the viewed object pass through a series of lenses and form an enlarged image of the object.
In the case of a SEM you do not see light but. The light ray from a mirror is reflected through the object or specimen into the objective lens which produces first magnification. The resolution of the image depends on the specimen being viewed not on the microscope being used.
As the beam scans the surface of the sample a highly magnified image is created which allows the system operator to view the samples microscopic features clearly. This real image is then magnified by the ocular lens or eyepiece to produce the virtual image. What you see when you look through a light microscope is a magnified image made from light reflecting off an object.
Magnifying powers of objectives are from 11 to 1001. Including more lenses doesnt change the basic principle of how a microscope magnifies but it does enable higher magnifications and gives a better quality image. The light rays which reflect off of the object are then focused into a magnified image.
This type of microscopy is a Phase-Contrast using two light beams passing through prisms. Condenser lenses in a light microscope. The image produced by the objective lens is then magnified again by the eyepiece lens which acts as a simple magnifying glass.
Click to see full answer. The specimen is normally placed close to the microscopic lens. They use lenses to focus light on the specimen magnifying it thus producing an image.
Focus the light transmitted by the specimen on the focal plane of the objective D. A light microscope can magnify images up to 1000x while electron microscopes can even magnify images more than 100000x Nester 2001. Two convex lenses can form a microscope.
A microscope must be able not only to magnify objects sufficiently but also to resolve or separate the fine details of the object that are of interest to the viewer. Magnification up to 1000x. Focus the image of the specimen on the objective focal plane E.
How does the resolution of a specimens image viewed under a compound light microscope a. Light from the object falls onto the objective lenses which creates a magnified image that is further magnified by the eyepieces. Direct light and reflected or diffracted light are brought together in phase peaks valleys match to form an image of the specimen.
A compound light microscope is a type of light microscope that uses a compound lens system meaning it operates through two sets of lenses to magnify the image of a specimen. The light microscope is an instrument for visualizing fine detail of an object. To collect the maximum amount of light from the object unite it and form a high quality magnified real image.
It uses a series of lenses to create a highly magnified image of the object. 16 Atomic force microscope The AFM is one of the foremost tools for imaging measuring and manipulating matter at the nanoscale. Create a magnified image of the specimen mounted on a transparent glass slide B.
A light microscope is a biology laboratory instrument or tool that uses visible light to detect and magnify very small objects and enlarge them. A light microscope is an instrument that creates a clear magnified image through a series of lenses. The compound microscope is also known as a biological microscope.

Parts Of A Microscope With Functions And Labeled Diagram

Anatomy Of The Microscope The Concept Of Magnification Olympus Ls

Microscopy How A Microscope Works Magnification Calculations How To Use A Microscope Slide Preparation Investigations Resolution Resolving Power Measuring Size Of Cell Electron Microscope Micrograph Light Micrograph Igcse O Level Gcse 9 1 Biology Revision
No comments for "Describe How a Light Microscope Creates a Magnified Image"
Post a Comment